Tony Awards 2024 Nominations: See the Complete List

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Live

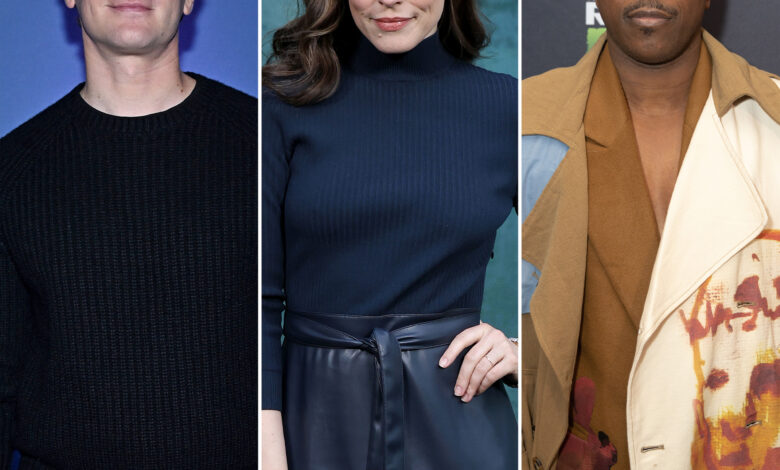
Jonathan Groff, Rachel McAdams, Leslie Odom Jr. Getty Images (3)
The moment theater fans have been waiting for arrived on Tuesday, April 30, when the nominations for the 2024 Tony Awards were announced.
Modern Family alum Jesse Tyler Ferguson and Hamilton‘s Renée Elise Goldsberry announced the nominations on Tuesday following the industry’s Drama Desk, Drama League and Outer Critics Circle Awards nominations earlier this season.
The 77th annual ceremony, which honors excellence in live Broadway theatre, will take place at Lincoln Center’s David H. Koch Theater in New York on Sunday, June 16. News broke in March that Ariana DeBose will return to host the awards show for the third time after previously helming the event in 2022 and 2023.
“I couldn’t pass up the chance to host the Tonys one more time at Lincoln Center,” DeBose, 33, said in a statement at the time. “I’m excited to collaborate with the team to create an incredible celebration of this season’s achievements on Broadway for our community and for everyone at home.”
When DeBose hosted the Tonys in June 2023, she had to come up with her own material due to the Writers Guild of America strike.
“Our siblings over at the WGA are currently on strike in pursuit of a fair deal,” she told the audience at the time. “Award shows are traditionally written by members of the WGA. In order for this show to go on, a whole host of people had to come together in order to find a compromise. And we are all here, so to every single person who had a hand in finding that compromise, I say a full-throated thank you!”
DeBose subsequently informed viewers that she would be ad-libbing her lines throughout the show. “So now you’re asking, what’s the compromise? Well, we don’t have a script, you guys. Yeah, I’m live and unscripted — you’re welcome,” she said. “So to anyone who may have thought last year was a bit unhinged, to them I say, ‘Darlings, buckle up.’”
She concluded: “But in all seriousness, yes, I am unscripted as is every presenter who comes on this stage tonight. We’re just making it up as we go along. And that’s cool. Again, it’s a blessing to be here.”
DeBose’s hosting gig last year came after her viral moment at the 2023 BAFTAs. That February, she received attention for her rap about the female nominees, particularly for her shout-out to Angela Bassett for doing “the thing.”
In June 2023, DeBose addressed the scrutiny surrounding her BAFTAs opening number. “Have I developed a little bit of stage fright? I would be lying if I said ‘no,’” she told Marie Claire. “But I also challenge myself and I do scary things every day. And if I’m afraid of something, I should probably do it.”
She continued: “I have found that trying to act as if I don’t feel something is not helpful. Pretending it’s not happening [is] not helpful. Yes, I performed at the BAFTAs. Yes, the Internet had a moment about it. Yes, some things were said that I didn’t appreciate and that I found very hurtful. And yes, eventually the tide turned on the Internet and people found what I saw in it: the fun, the joy. But that doesn’t mean that along that little journey, I didn’t feel my feelings about having the internet make fun of me for being me and doing what I love to do. I don’t understand that part of society.”
Keep scrolling to see the complete list of this year’s Tony nominees:
Best Musical
Hell’s Kitchen
Illinoise
The Outsiders
Suffs
Water for Elephants
Best Performance by a Leading Actor in a Musical
Brian d’Arcy James, Days of Wine and Roses
Brody Grant, The Outsiders
Jonathan Groff, Merrily We Roll Along
Dorian Harewood, The Notebook
Eddie Redmayne, Cabaret
Best Performance by a Leading Actress in a Musical
Eden Espinoza, Lempicka
Maleah Joi Moon, Hell’s Kitchen
Kelli O’Hara, Days of Wine and Roses
Gayle Rankin, Cabaret at the Kit Kat Club
Best Play
Jaja’s African Hair Braiding
Mary Jane
Mother Play
Prayer for the French Republic
Stereophonic
Best Performance by a Leading Actor in a Play
William Jackson Harper, Uncle Vanya
Leslie Odom, Jr., Purlie Victorious
Liev Schreiber, Doubt
Jeremy Strong, An Enemy of the People
Michael Stuhlbarg, Patriots
Best Performance by a Leading Actress in a Play
Betsy Aidem, Prayer for the French Republic
Jessica Lange, Mother Play
Rachel McAdams, Mary Jane
Sarah Paulson, Appropriate
Amy Ryan, Doubt
Best Performance by a Featured Actor in a Musical
Roger Bart, Back To The Future: The Musical
Joshua Boone, The Outsiders
Brandon Victor Dixon, Hell’s Kitchen
Sky Lakota-Lynch, The Outsiders
Daniel Radcliffe, Merrily We Roll Along
Steven Skybell, Cabaret at the Kit Kat Club
Best Performance by a Featured Actress in a Musical
Shoshana Bean, Hell’s Kitchen
Amber Iman, Lempicka
Nikki M. James, Suffs
Leslie Rodriguez Kritzer, Monty Python’s Spamalot
Kecia Lewis, Hell’s Kitchen
Lindsay Mendez, Merrily We Roll Along
Bebe Neuwirth, Cabaret at the Kit Kat Club
Best Performance by a Featured Actor in a Play
Will Brill, Stereophonic
Eli Gelb, Stereophonic
Jim Parsons, Mother Play
Tom Pecinka, Stereophonic
Corey Stoll, Appropriate
Best Performance by a Featured Actress in a Play
Quincy Tyler Bernstine, Doubt: A Parable
Juliana Canfield, Stereophonic
Celia Keenan-Bolger, Mother Play
Sarah Pidgeon, Stereophonic
Kara Young, Purlie Victorious: A Non-Confederate Romp Through the Cotton Patch
Best Choreography
Camille A. Brown, Hell’s Kitchen
Annie-B Parson, Here Lies Love
Rick Kuperman and Jeff Kuperman, The Outsiders
Justin Peck, Illinoise
Jesse Robb and Shana Carroll, Water for Elephants
Best Direction of a Musical
Maria Friedman, Merrily We Roll Along
Michael Greif, Hell’s Kitchen
Leigh Silverman, Suffs
Jessica Stone, Water for Elephants
Danya Taymor, The Outsiders
Best Direction of a Play
Daniel Aukin, Stereophonic
Anne Kauffman, Mary Jane
Kenny Leon, Purlie Victorious
Lila Neugebauer, Appropriate
Whitney White, Jaja’s African Hair Building
Best Revival of a Musical
Cabaret at the Kit Kat Club
Gutenberg! The Musical!
Merrily We Roll Along
Best Revival of a Play
Appropriate
An Enemy of the People
Purlie Victorious
Best Book of a Musical
Kristoffer Diaz, Hell’s Kitchen
Bekah Brunstetter, The Notebook
Adam Rapp and Justin Levine, The Outsiders
Shaina Taub, Suffs
Rick Elice, Water for Elephants
Best Original Score
Adam Guettel, Days of Wine and Roses
David Byrne and Fatboy Slim, Here Lies Love
Will Butler, Stereophonic
Shaina Taub, Suffs
Jamestown Revival, The Outsiders
Best Scenic Design in a Musical
AMP featuring Tatiana Kahvegian, The Outsiders
Robert Brill and Peter Nigrini, Hell’s Kitchen
Takeshi Kata, Water for Elephants
David Korins, Here Lies Love
Riccardo Hernandez and Peter Nigrini, Lempicka
Tim Hatley and Finn Ross, Back to the Future: The Musical
Tom Scutt, Cabaret at the Kit Kat Club
Best Scenic Design in a Play
dots, Appropriate
dots, An Enemy of the People
Derek McLaine, Purlie Victorious
David Zinn, Jaja’s African Hair Braiding
David Zinn, Stereophonic
Best Costume Design in a Musical
Dede Ayite, Hell’s Kitchen
Linda Cho, The Great Gatsby
David Israel Reynoso, Water for Elephants
Tom Scutt, Cabaret at the Kit Kat Club
Paul Tazewell, Suffs
Best Costume Design in a Play
Dede Ayite, Appropriate
Dede Ayite, Jaja’s African Hair Braiding
Enver Chakartash, Stereophonic
Emilio Sosa, Purlie Victorious
David Zinn, An Enemy of the People
Best Lighting Design in a Musical
Brandon Stirling Baker, Illinoise
Isabella Byrd, Cabaret at the Kit Kat Club
Natasha Katz, Hell’s Kitchen
Bradley King and David Bengali, Water for Elephants
Brian MacDevitt and Hana S. Kim, The Outsiders
Best Lighting Design in a Play
Isabella Byrd, An Enemy of the People
Amith Chandrashaker, Prayer for the French Republic
Jiyoun Chang, Stereophonic
Jane Cox, Appropriate
Natasha Katz, Grey House
Best Sound Design of a Musical
M.L. Dogg and Cody Spencer, Here Lies Love
Kai Harada, Merrily We Roll Along
Nick Lidster for Autograph, Cabaret at the Kit Kat Club
Gareth Owen, Hell’s Kitchen
Cody Spencer, The Outsiders
Best Sound Design of a Play
Justin Ellington and Stefania Bulbarella, Jaja’s African Hair Braiding
Leah Glee, Mary Jane
Tom Gibbons, Grey House
Bray Poor and Will Pickens, Appropriate
Ryan Rumery, Stereophonic
Best Orchestrations
Timo Andres, Illinoise
Will Butler and Justin Craig, Stereophonic
Justin Levine, Matt Hinkley and Jamestown Revival, The Outsiders
Tom Kitt and Adam Blackstone, Hell’s Kitchen
Jonathan Tunick, Merrily We Roll Along
The 77th annual Tony Awards will air on CBS Sunday, June 16, at 8 p.m. ET.