What happens when you trigger a car’s automated emergency stopping?


Mercedes-Benz
Most car accidents begin and end in a few seconds. That’s plenty of time to get in a tiny micro-nap while driving. The famous asleep-at-the-wheel film scene in National Lampoon’s Vacation, where Clark Griswold goes off to slumberland for 72 seconds while piloting the Wagon Queen Family Truckster (a paragon of automotive virtue but lacking any advanced driver safety systems), might be a comical look at this prospect. But if Clark were in the real world, he and his family would likely have been injured or killed—or they could have caused similar un-funny consequences for other motorists or pedestrians.
There’s plenty of real-world news on the topic right now. Early in 2023, the Automobile Association of America’s Foundation for Traffic Safety published a study estimating that 16–21 percent of all fatal vehicle crashes reported to police involve drowsy driving.
With the road fatality numbers in the US hovering close to 38,000 over the past few years, that means between 6,080 and 7,980 road deaths are linked to drowsy drivers. Further research by the AAA’s Foundation finds that drivers likely under-report drowsiness in all car crashes. Nodding off while driving is as dangerous as—and potentially more dangerous than—driving drunk. And while drunk-driving figures have decreased between 1991 and 2021, the opposite is true for drowsy driving.
Nissan
Automakers have not been unaware of the problem, either. As long ago as 2007, manufacturers like Volvo began offering drowsiness-detection systems that monitored the driver, though in a simpler way than what’s seen in the leading systems of today. They sensed the velocities of inputs to steering, throttle, and brakes. Some even used a camera aimed at the driver to discern if drivers were becoming inattentive, including drooping their head or simply averting their view from the straight-ahead.
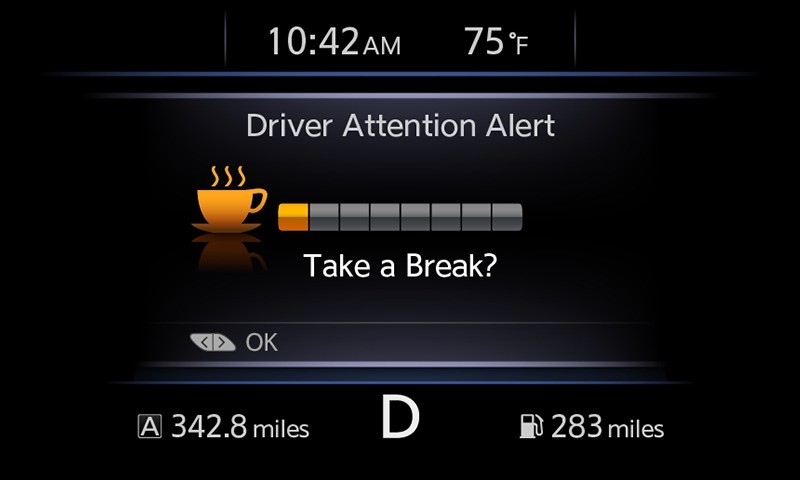
These systems chime a warning and project a visual alert on the dashboard asking if the driver wants to take a break, often with the universal symbol for wakefulness—a coffee cup—appearing in the instrument cluster. Many new cars today still have this feature. And to be sure, it was then, is now, and forever will be a beneficial and effective method of alerting drivers to their drowsiness.
But a level beyond the above audible and visual cues has changed this landscape of blunting the upward trend of drowsy driving. As Level-2, semi-autonomous capabilities emerge in medium- and even lower-priced automobiles, these features also allow cars and SUVs to take control of the vehicle should the vehicle determine that the driver has become inattentive or incapacitated.
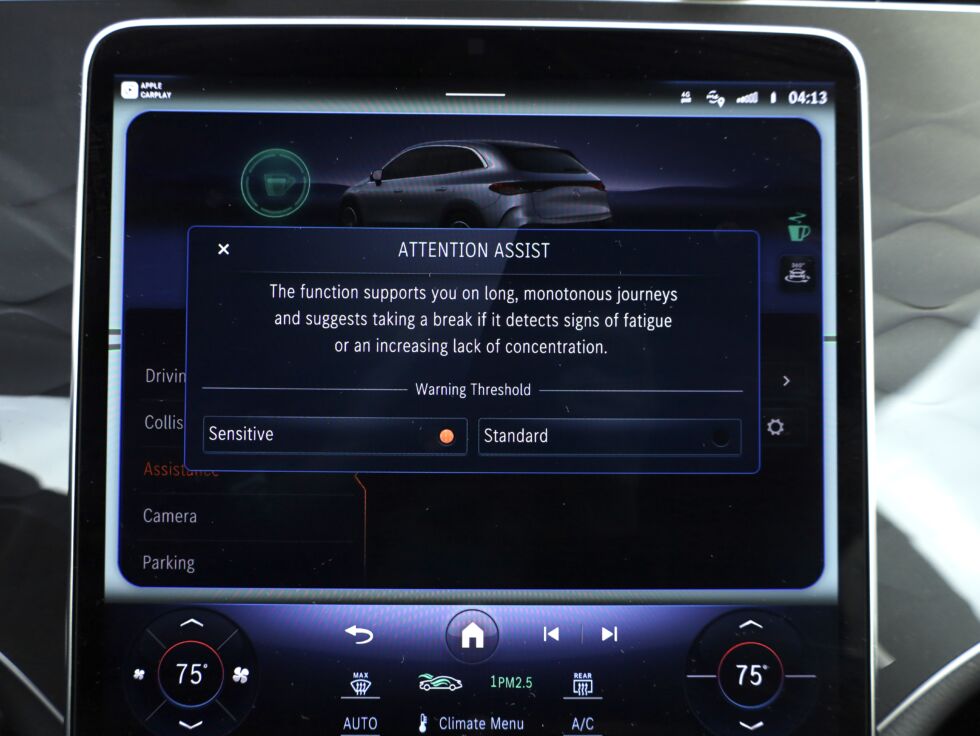
Enlarge / On some vehicles, like this Mercedes, you can select the sensitivity of the drowsy driver program (“Attention Assist” in this case) to have a lower or higher threshold for activation.
Jim Resnick
Because all the pieces of a vehicle-control puzzle are already on board, enabling a system to take over from an inattentive driver is a matter of programming—extensive programming, of course, but all the critical pieces of hardware are often already there:
- Selective braking from adaptive cruise control and stability control
- Self-steering functions of lane-keeping and lane-centering
- A cellular telematics network.
It’s a lengthy programming exercise that can take control of a vehicle in a simplified way, but not before three forms of human stimuli are triggered to wake up a drowsy driver: sight, sound, and a physical prompt.
This is all great in theory and in a digital vacuum, but I wanted to explore what occurs inside a car that has determined that the driver is no longer actually driving. The Infiniti QX60 and Mercedes EQE 350 have such emergency stop capabilities; I recently tested both.


